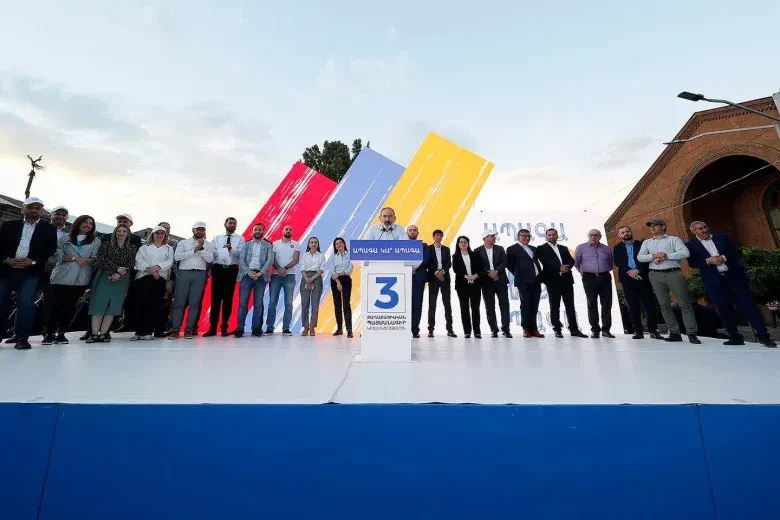
The fact "Fact" writes The fact that such a division is artificial, but we have not once touched upon it. It is no less dangerous that he is trying to show that after the 44-day war, a satisfactory situation has been created, which leads to peace. In other words, we entered the long-awaited "Age of Peace". As a result of the management of politics.
From the beginning of the 1990s to 2020, as they were fragile, the Artsakh issue provided a certain security balance, and its status quoided to pursue a relatively predictable foreign and domestic identity. In the field, despite the existing pressure and opposition-government tensions, there was some institutional stability. The unwritten rules of the game between the government and the opposition allowed the political crises to solve without destructive shocks for statehood. Civil society, media, community of experts and academic circles formed a certain atmosphere of public control and political pluralism. Although the issues of weakness and social polarization of corruption, the party system have always been in the context of external threats and national security. Despite many complaints in the field of social policy, statehood ensured minimal guarantees in the fields of disability, poverty, pensions and healthcare. From the point of view of foreign policy, Armenia skillfully balanced the interests of Russia, West and other regional actors. The military-political alliance with the Russian side, the EEU and CSTO membership, as well as the developing relations with the EU and the partnership with the United States allowed Armenia to work in different directions. And the format of the international mediation in the Artsakh issue (Minsk Group) created an area of the diplomatic chess game, where Armenia's position was mainly perceived as a defense, but on the other hand, given the factor of defending the interests of the people of Artsakh. This multi-vector foreign policy allowed Armenia to be on the agenda of both Russia and the European Union, the United States, Iran and other partners. Thus, the territorial smallness, resource lack of resources was partially compensated in terms of political flexibility and the lack of foreign markets, Armenia was able to provide some economic stability, based on the rapid development of the IT sector, the growth of the Diaspora, the growth of foreign labor, and small and medium-sized businesses. On the other hand, some success have been achieved in the direction of economic diversification, stabilization of the financial system and fiscal discipline. Economic policy depends on external factors, and socio-economic tension, but there was the establishment of the business, health environment, and the Armenian side, the Armenian side, due to the army's combat government, and the public. The presence of consolidation, as well as the presence of the Russian military base, was able to keep the military balance. Despite the constant tension, the Artsakh Status Quo was considered to be a sharp change in the scope of the region's war. The defeat in the war and the resulting situation completely transformed Armenia's domestic and external situation, revealing systemic shortcomings, weakness of the national security strategy and the dangerous tendencies of the public's unity loss. As a result of the war, the Armenian side was not only lost in Artsakh, which has been deprived of the security zone, and more than 120,000 Artsakh critics have been released in Armenia. The political field was extremely divided, and the opposition and the government entered the phase of mutual crimes and regular crises. All segments of society, including youth, intelligentsia, state officers, have appeared to the new wave of misconduct, despair, and the new wave of emigration. Socio-economic problems have escalated, and the quality of state services has decreased due to the low financial resources, the increase in social burden and the decline in management efficiency. It is no coincidence that the crisis in domestic political life is regularly deepened in domestic political life after the Artsakh war. Extraordinary elections are taking place, the wave of political persecution increases, the public division continues to deepen, and the degradation of political institutions continues. Armenia's position in the political sphere is unprecedented. As a result of the war, Armenia lost not only Artsakh's de facto independence, but also its regional role, reliability and multi-vector policy with foreign partners. In relations with Russia, which were associated with the fact that the main security guarantor was, an atmosphere of mutual distrust and coldness was formed. Western partners, although some support promised to Armenia, did not have enough tools and will to influence regional processes. Turkey and Azerbaijan, using Armenia's weakening, strengthened their position in the South Caucasus, and Iran was almost powerless to influence the events. Thus, Armenia's foreign policy is in the absence of uncertainty, tremors and strategic perspective, to deprive the opportunity of foreign policy maneuvers and depending on the will of the external actors. Artsakh's loss, uncertainty of the security zone, the continuity of border incidents. Through consolidation, institutional reconstruction and restoration of the national dream. But it is impossible during these authorities. They are in full opposite way. Arsen Sahakyan