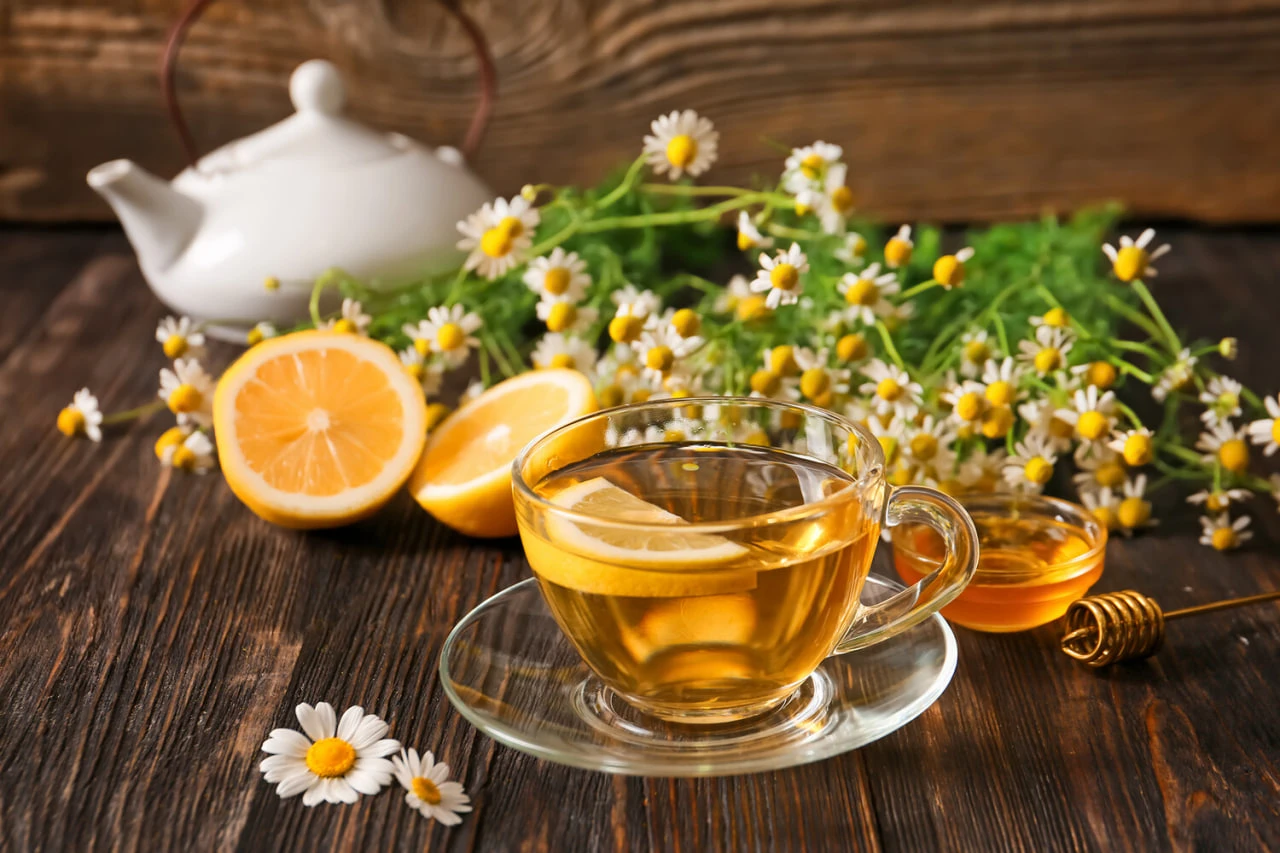
Chamomile's anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties are comparable to those of pain relievers. Scientists from the USA and Japan came to this conclusion. The results of a large-scale meta-analysis were published in the journal Pharmaceutical Biology.
The authors analyzed data from 11 randomized clinical trials in which chamomile-based preparations were used to treat mucositis, oral infections, and gastrointestinal inflammation. Chamomile extract significantly reduced pain, swelling, and inflammation, and accelerated tissue repair. The effect was statistically significant and comparable to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, but without their typical side effects.
Chamomile has shown its greatest effectiveness in the treatment of mucositis, an inflammation of the mucosa that often occurs after chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Scientists attribute the plant's healing properties to its active ingredients, namely bisabolol and apigenin, which suppress the production of inflammatory cytokines and stimulate tissue regeneration.
According to the researchers, chamomile could become a safe and affordable alternative for the treatment of chronic inflammation and could also be used in preventive and cosmetic products.
Translation:Euromedia24.com-in: